Environment variables
Environment variables can be used to customize the behavior of a dbt project depending on where the project is running. See the docs on
env_var for more information on how to call the jinja function {{env_var('DBT_KEY','OPTIONAL_DEFAULT')}} in your project code.
Environment variables in dbt Cloud must be prefixed with either DBT_ or DBT_ENV_SECRET or DBT_ENV_CUSTOM_ENV_. Environment variables keys are uppercased and case sensitive. When referencing {{env_var('DBT_KEY')}} in your project's code, the key must match exactly the variable defined in dbt Cloud's UI.
Setting and overriding environment variables
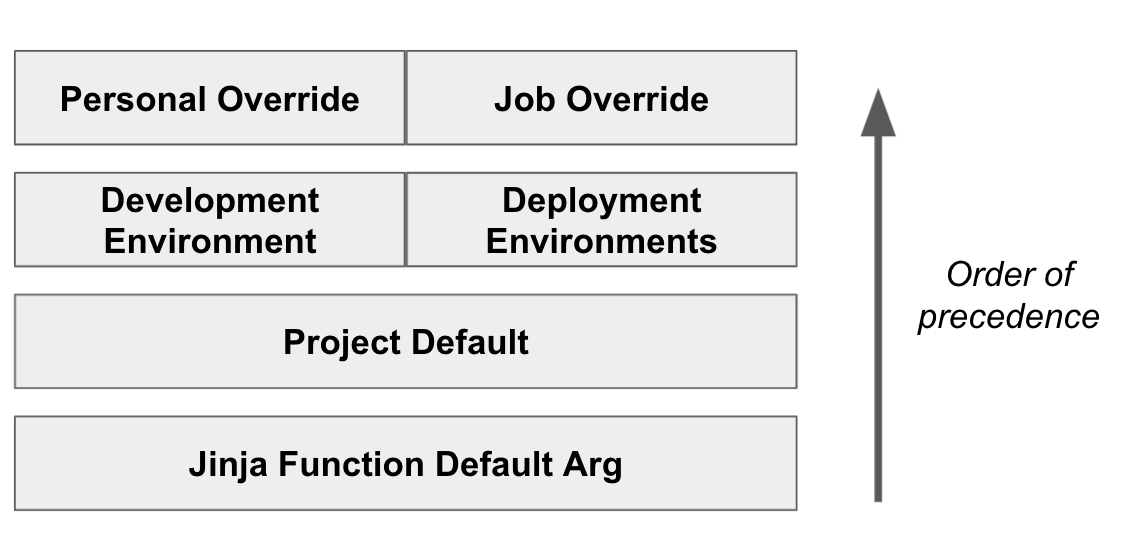
Order of precedence
Environment variable values can be set in multiple places within dbt Cloud. As a result, dbt Cloud will interpret environment variables according to the following order of precedence (lowest to highest):
There are four levels of environment variables:
- The optional default argument supplied to the
env_varJinja function in code, which can be overridden at (lowest precedence) - The project-wide level by its default value, which can be overridden at
- The environment level, which can in turn be overridden again at
- The job level (job override) or in the IDE for an individual dev (personal override). (highest precedence)
Setting environment variables at the project and environment level
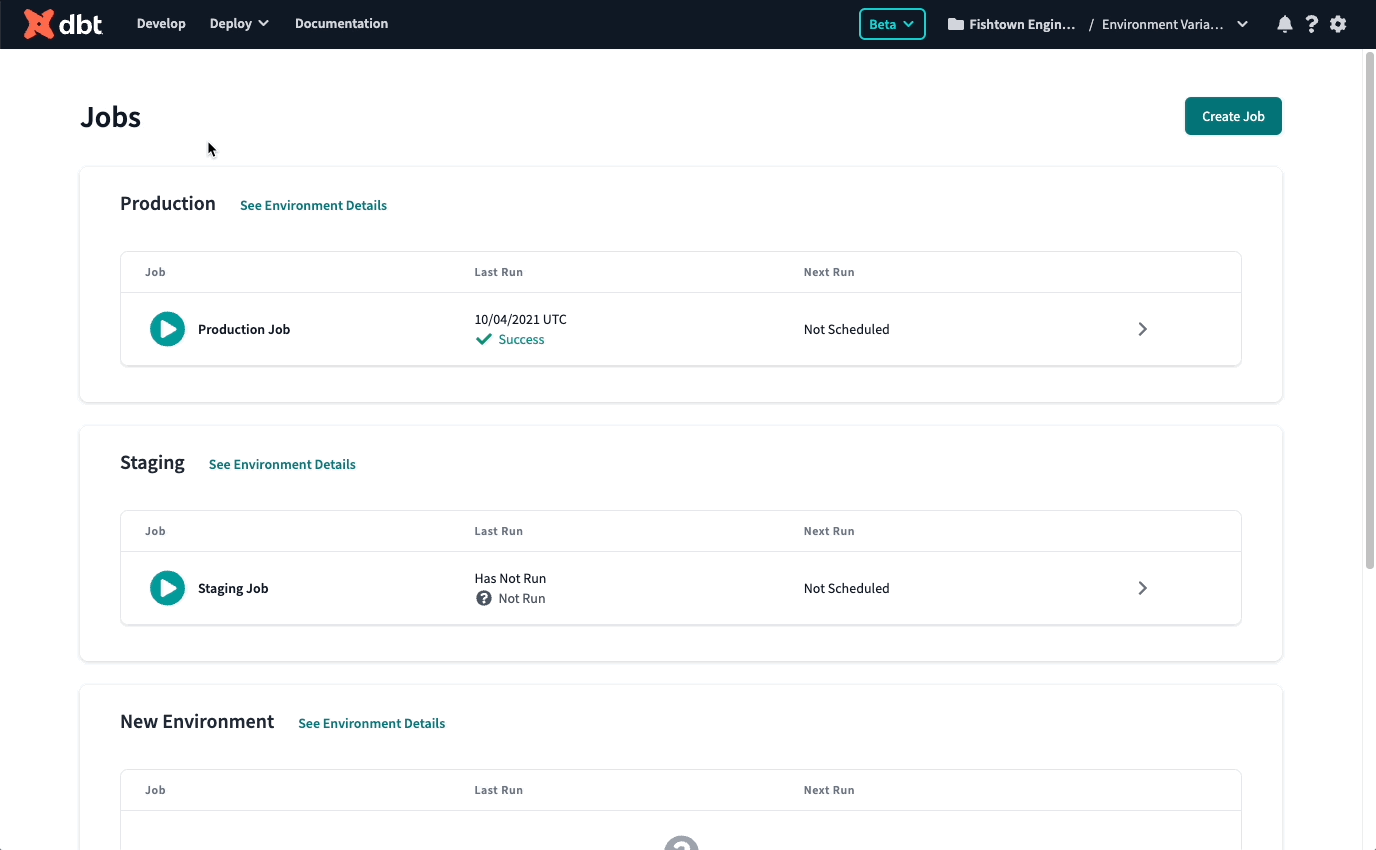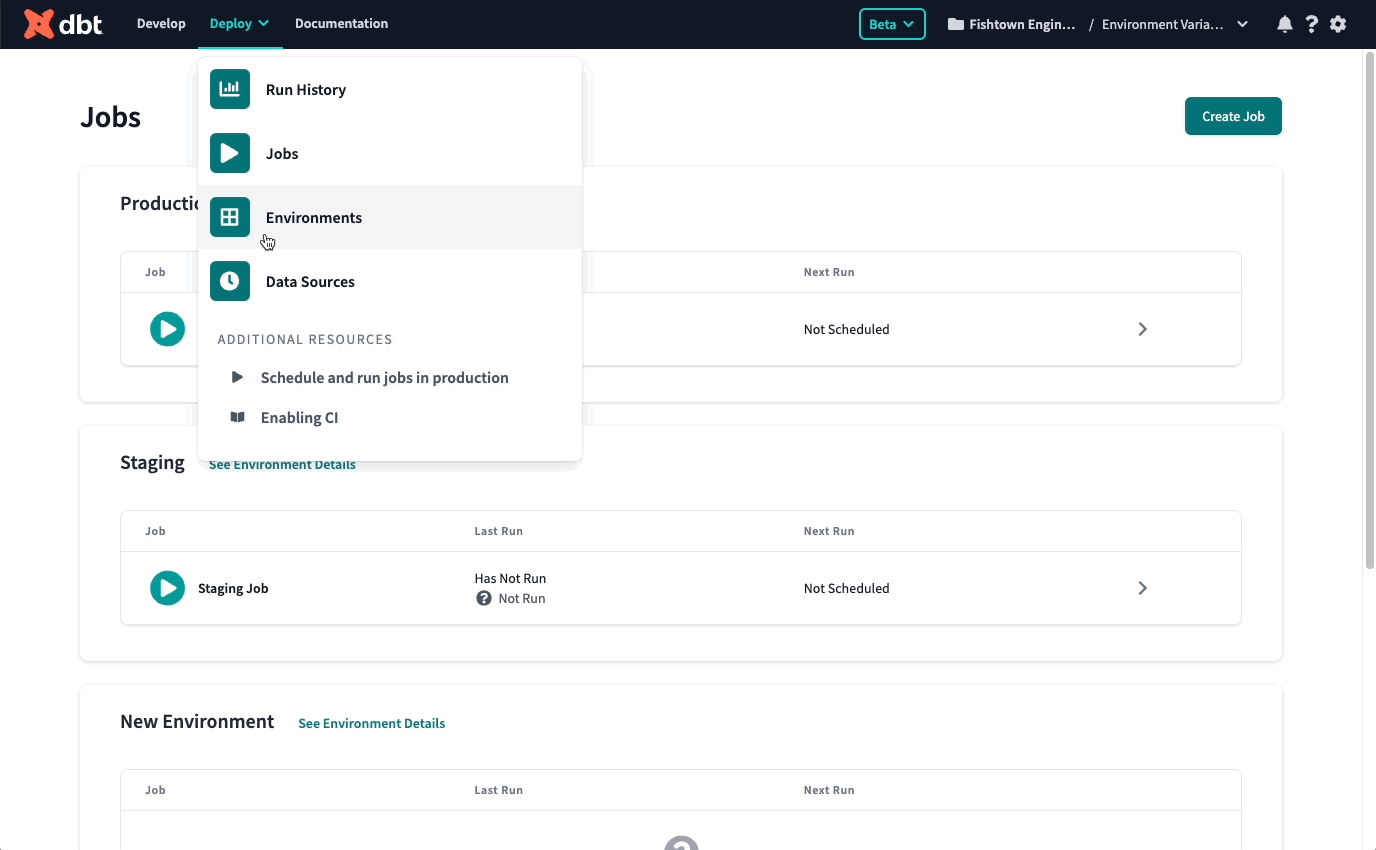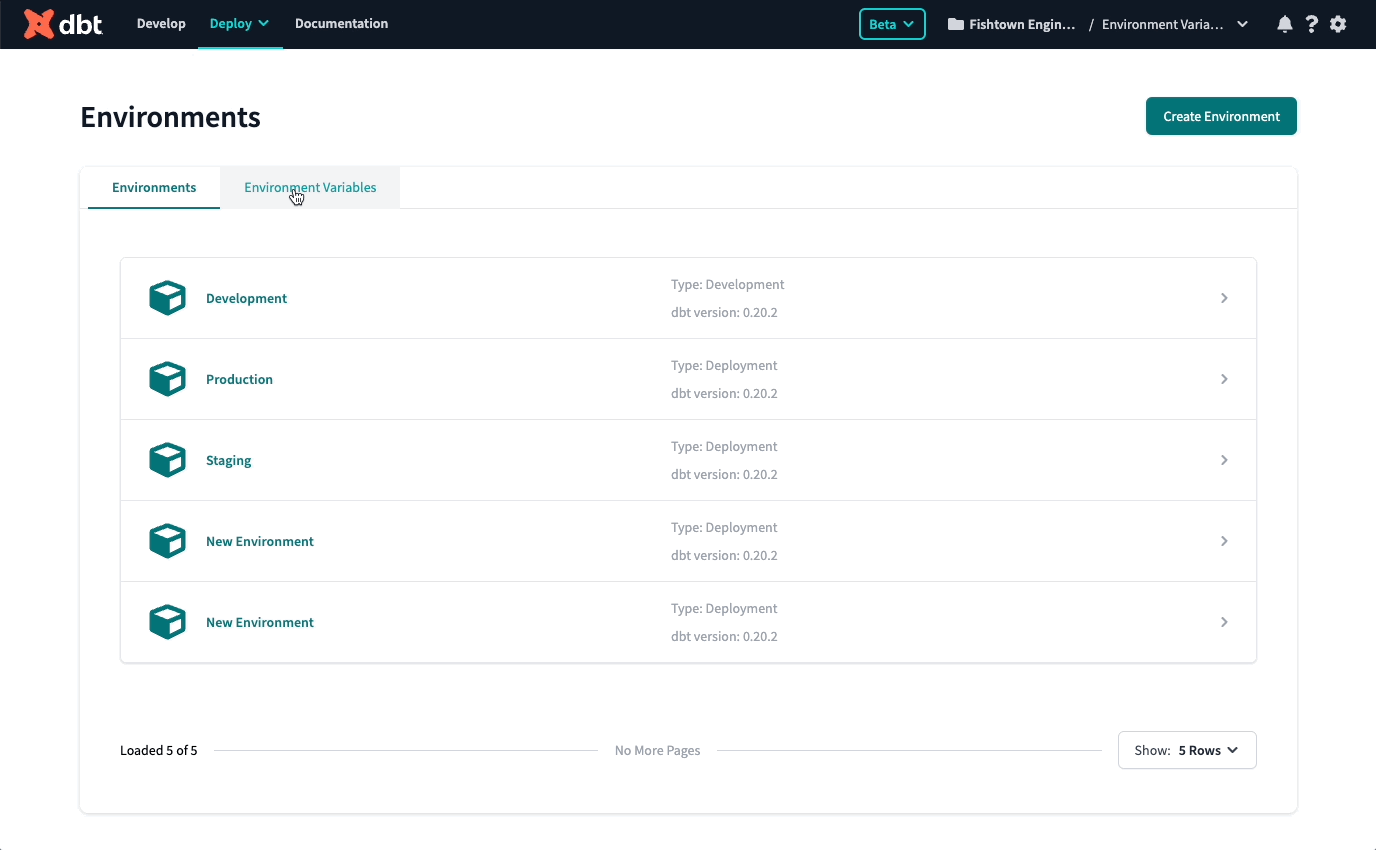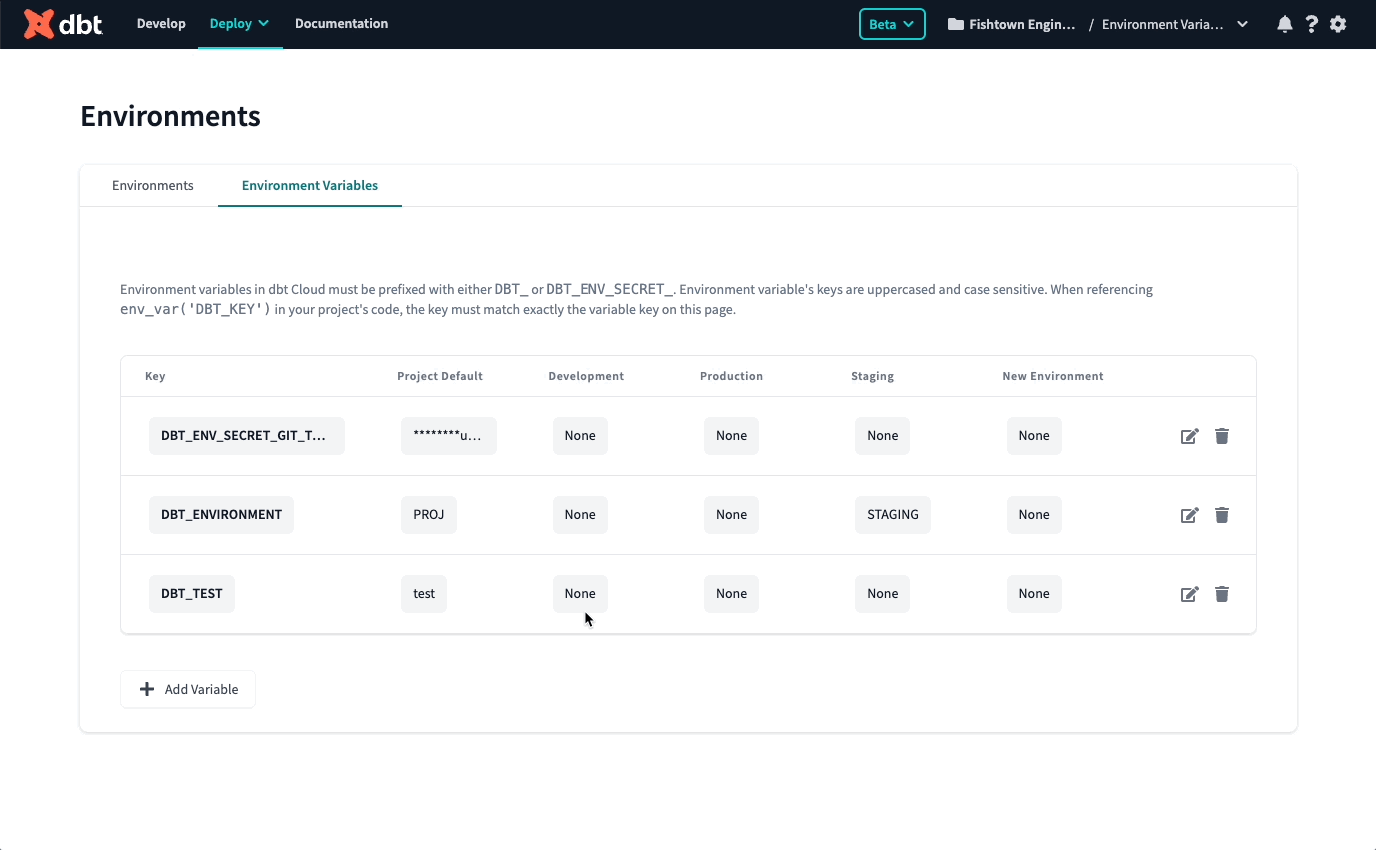
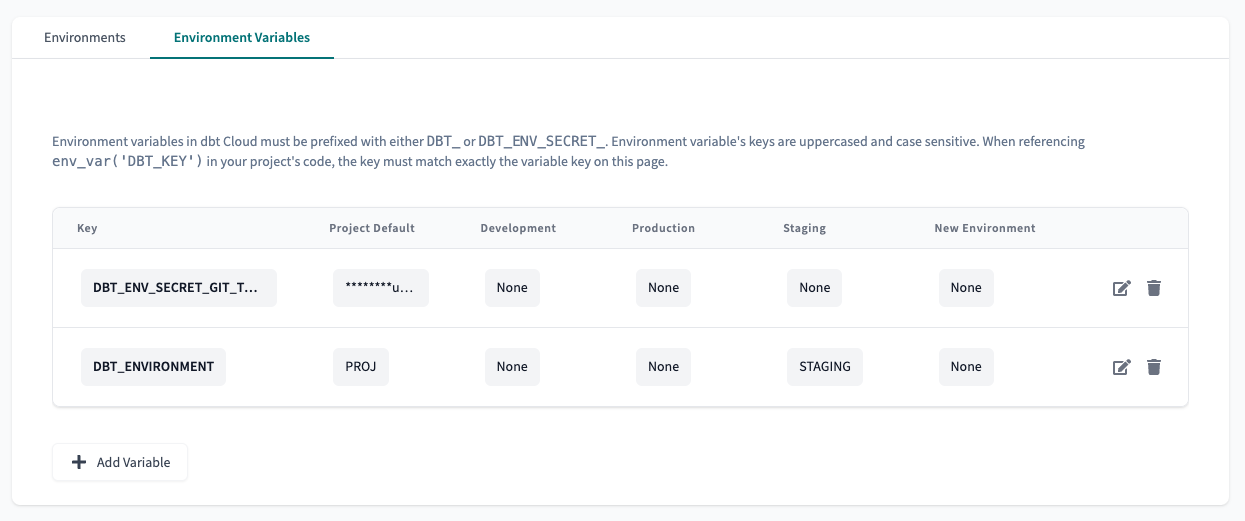
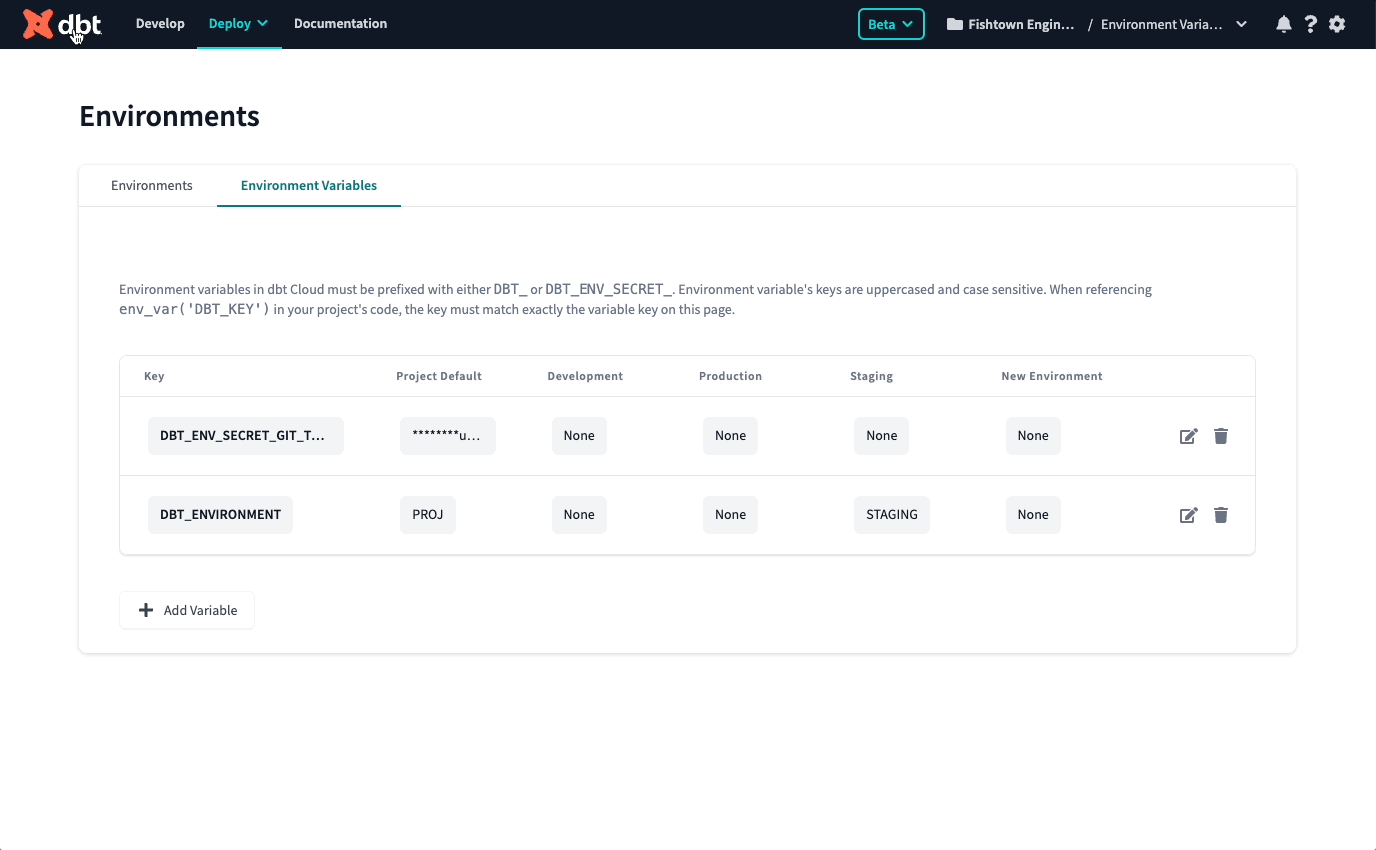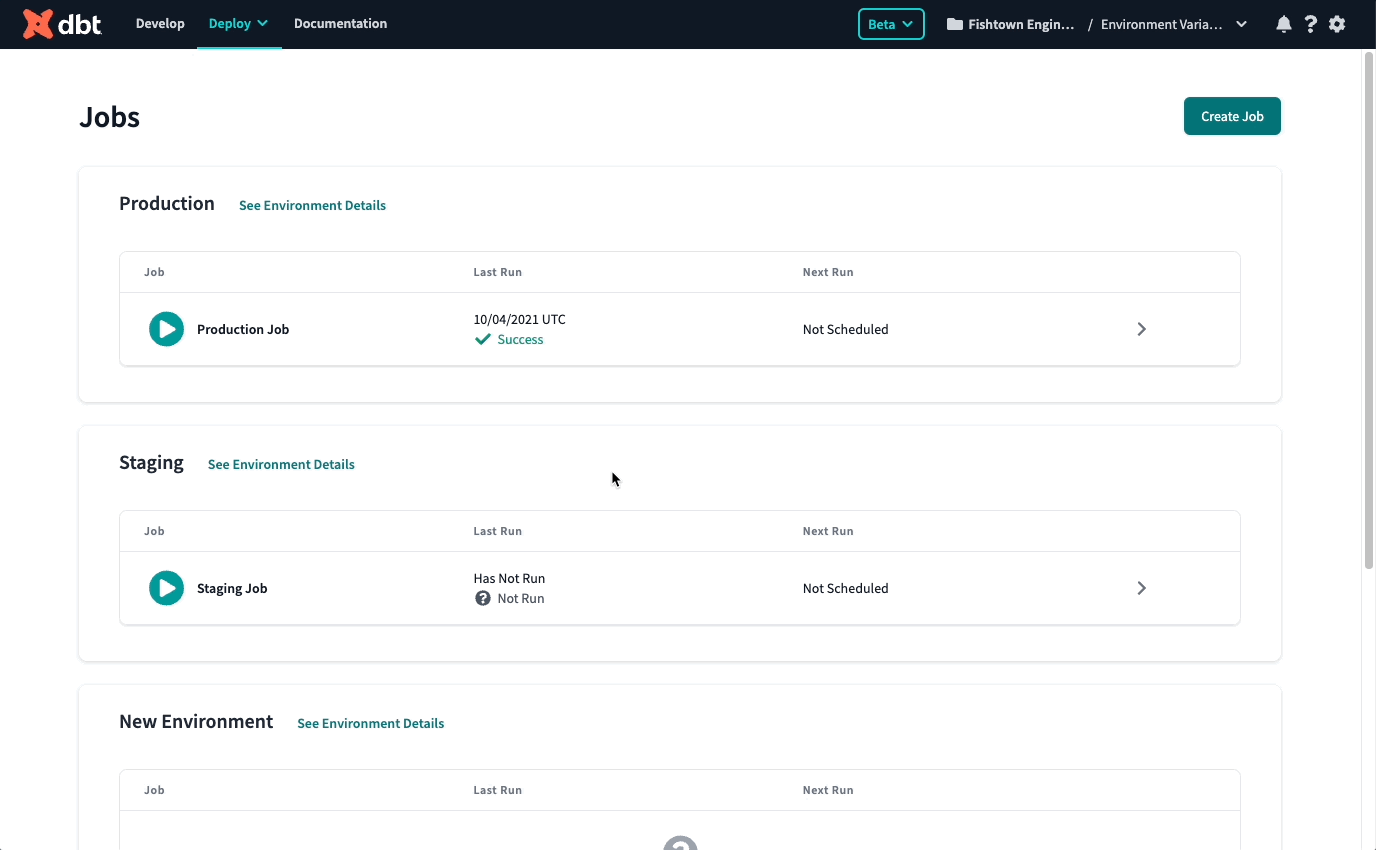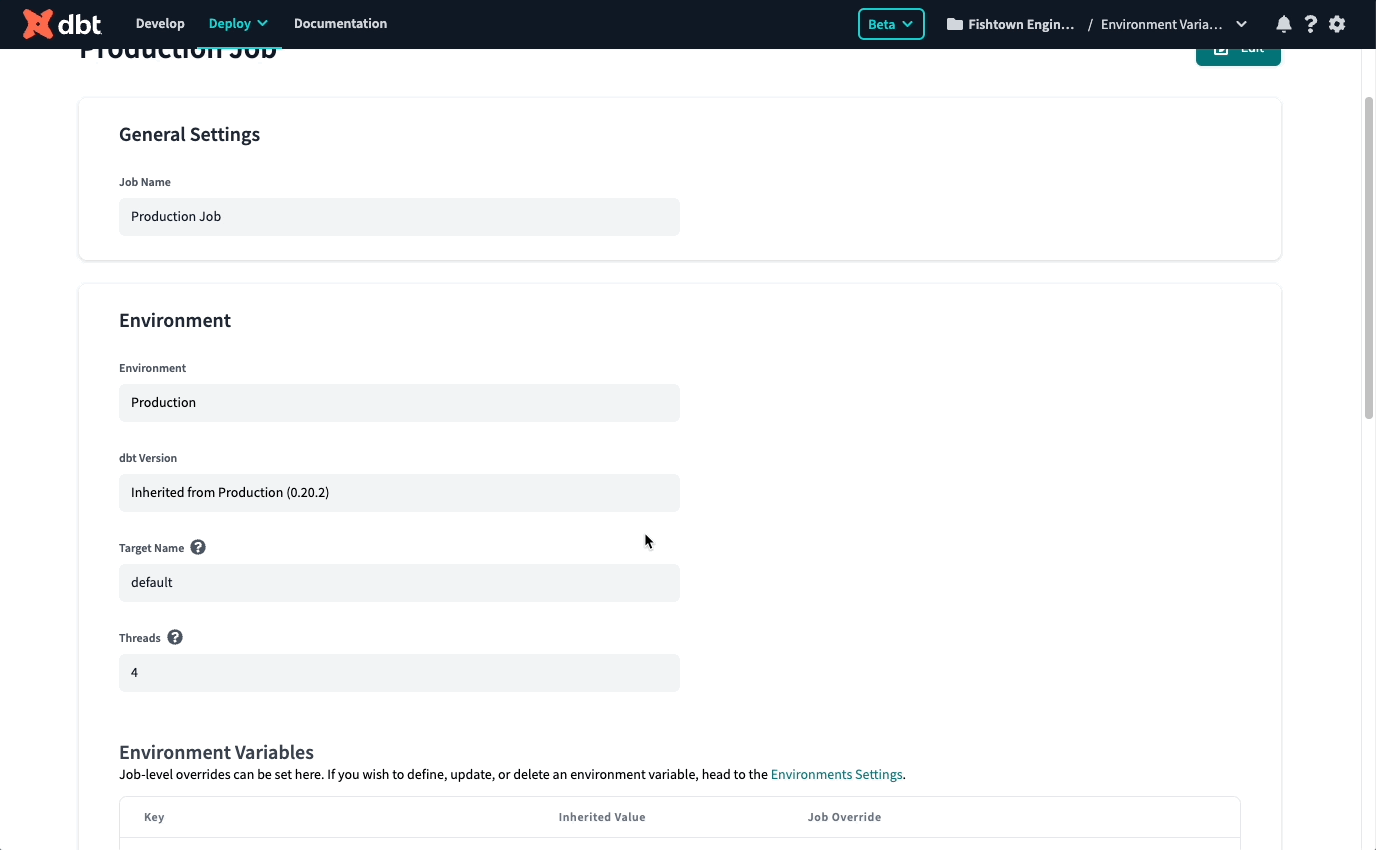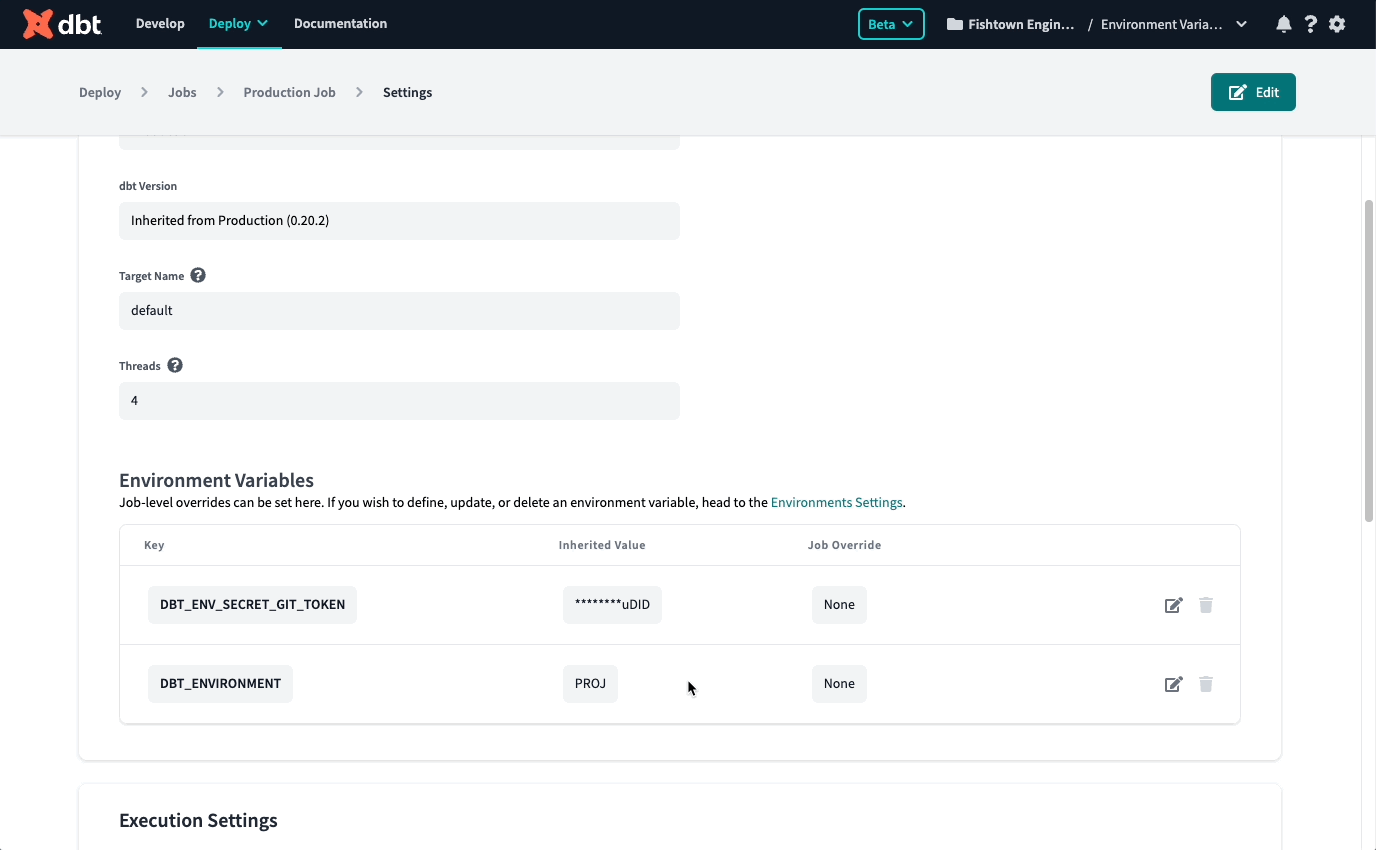
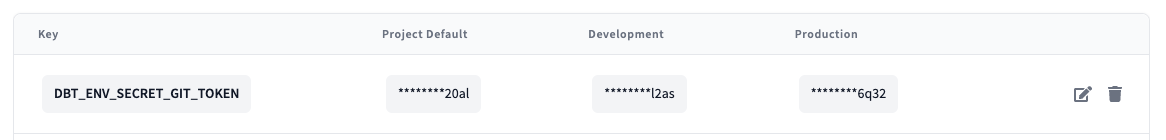
To set environment variables at the project and environment level, click Deploy in the top left, then select Environments. Click Environments Variables to add and update your environment variables.
You'll notice there is a Project Default column. This is a great place to set a value that will persist across your whole project, independent of where the code is run. We recommend setting this value when you want to supply a catch-all default or add a project-wide token or secret.
To the right of the Project Default column are all your environments. Values set at the environmental level take priority over the project-level default value. This is where you can tell dbt Cloud to interpret an environment value differently in your Staging vs. Production environment, as an example.
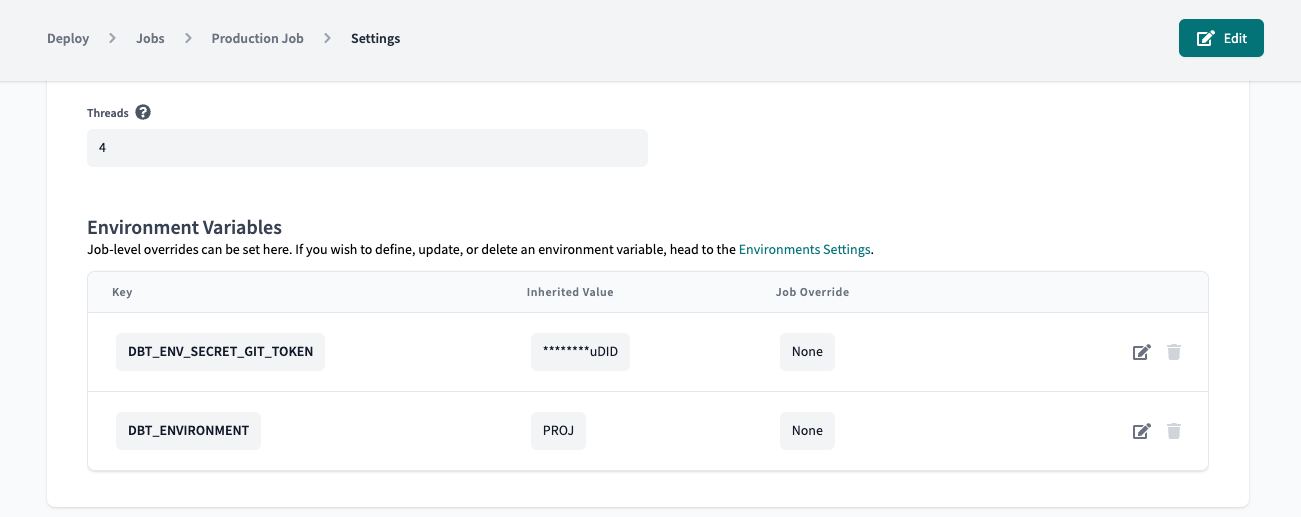
Overriding environment variables at the job level
You may have multiple jobs that run in the same environment, and you'd like the environment variable to be interpreted differently depending on the job.
When setting up or editing a job, you will see a section where you can override environment variable values defined at the environment or project level.
Every job runs in a specific, deployment environment, and by default, a job will inherit the values set at the environment level (or the highest precedence level set) for the environment in which it runs. If you'd like to set a different value at the job level, edit the value to override it.
Overriding environment variables at the personal level
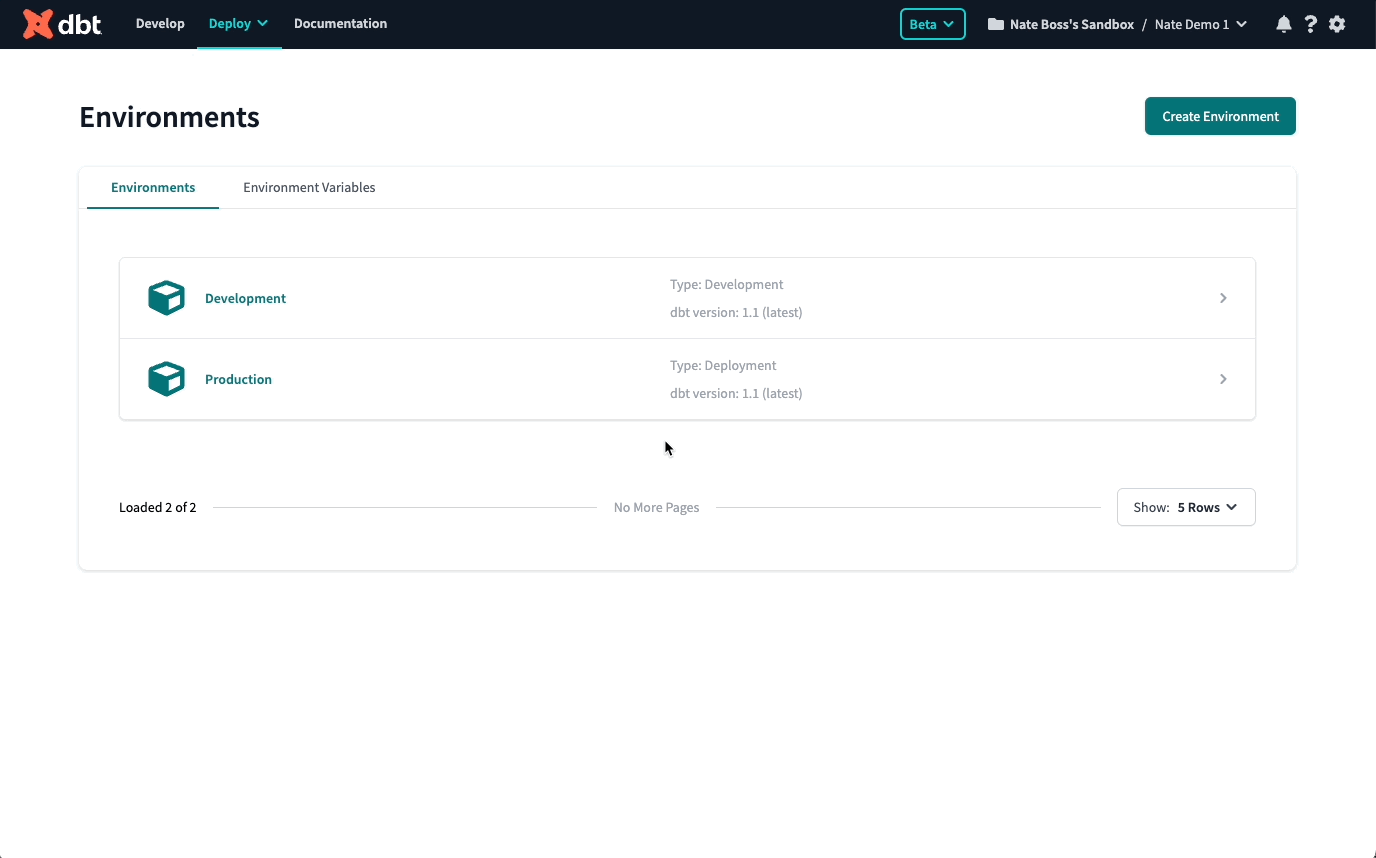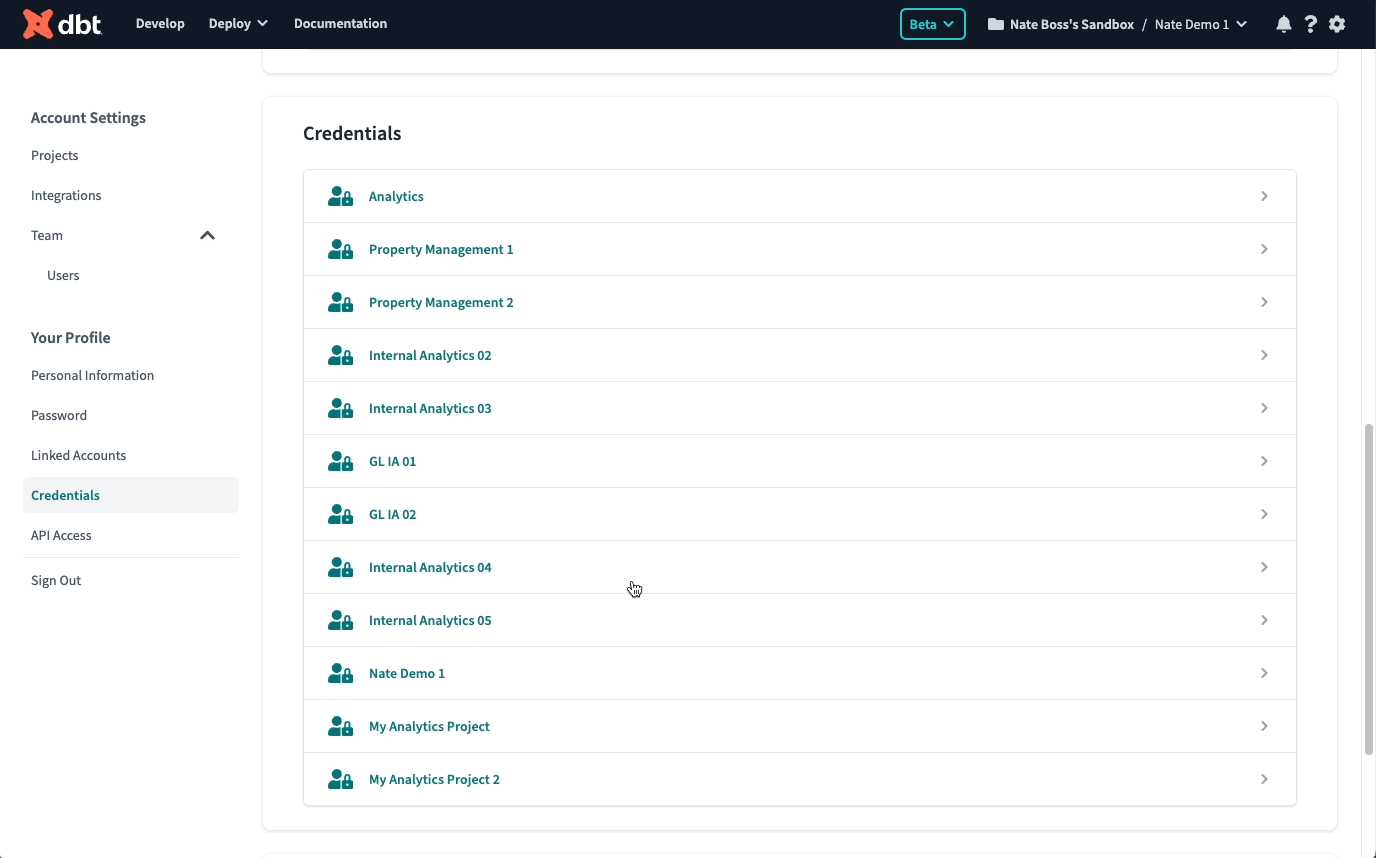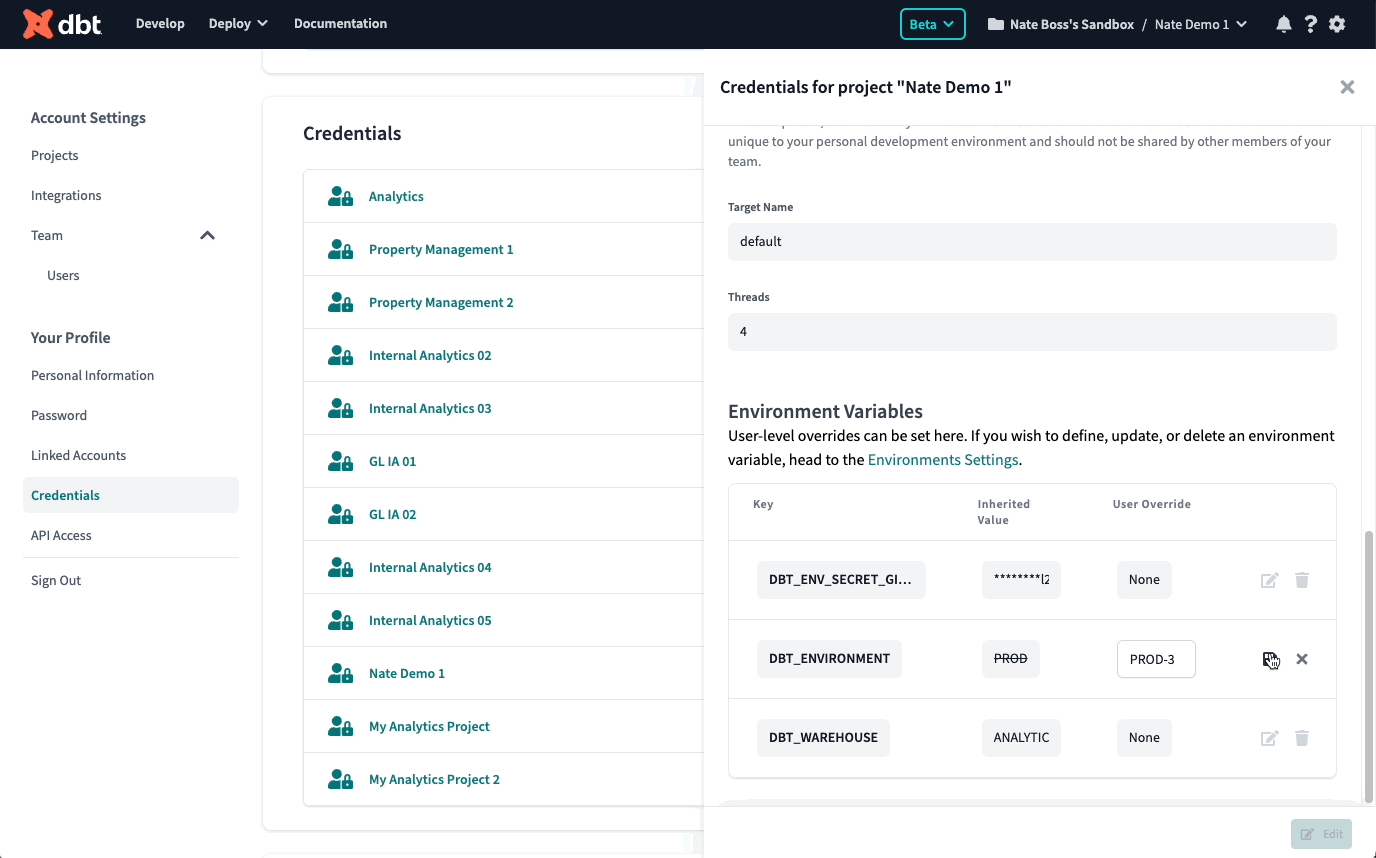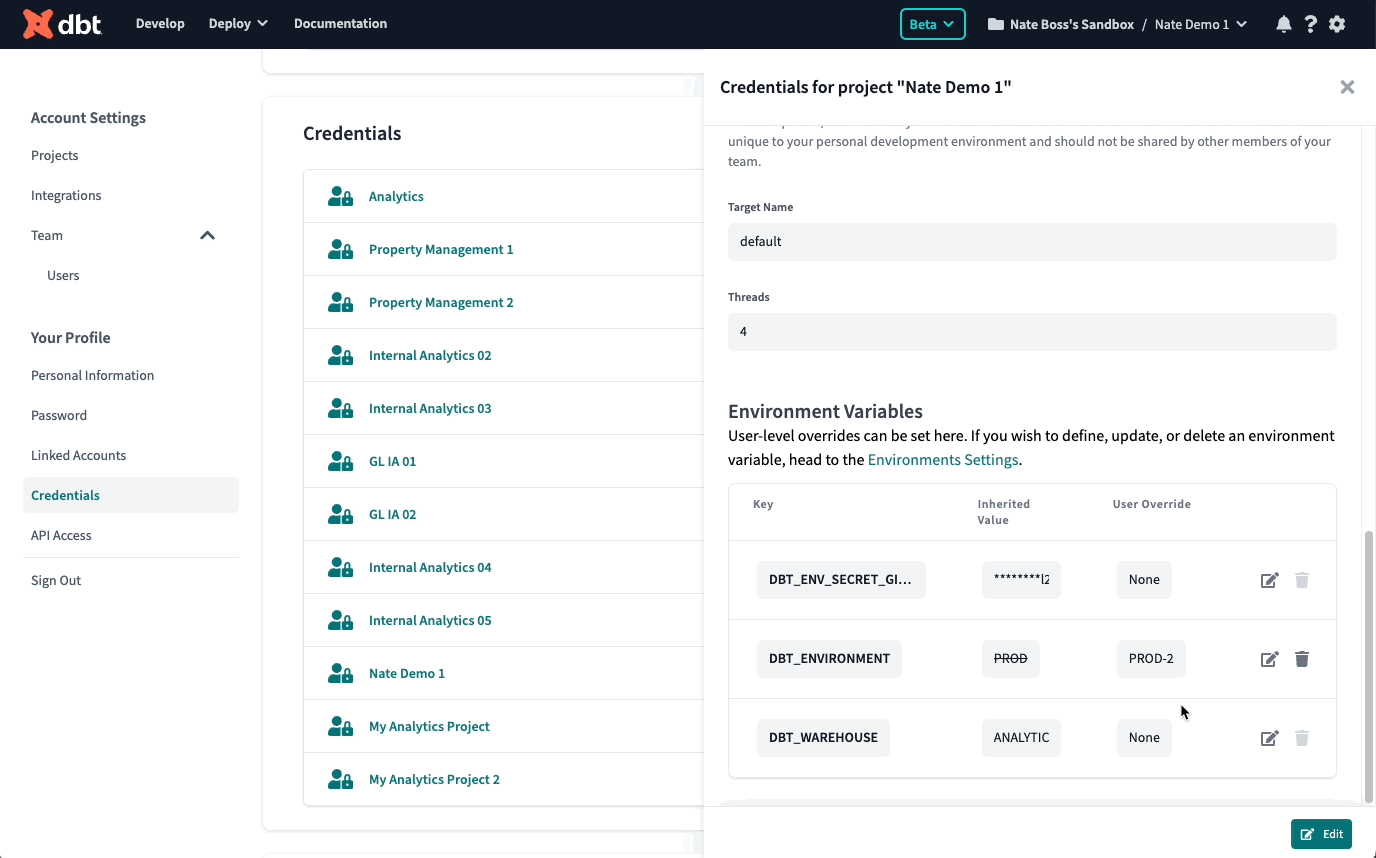
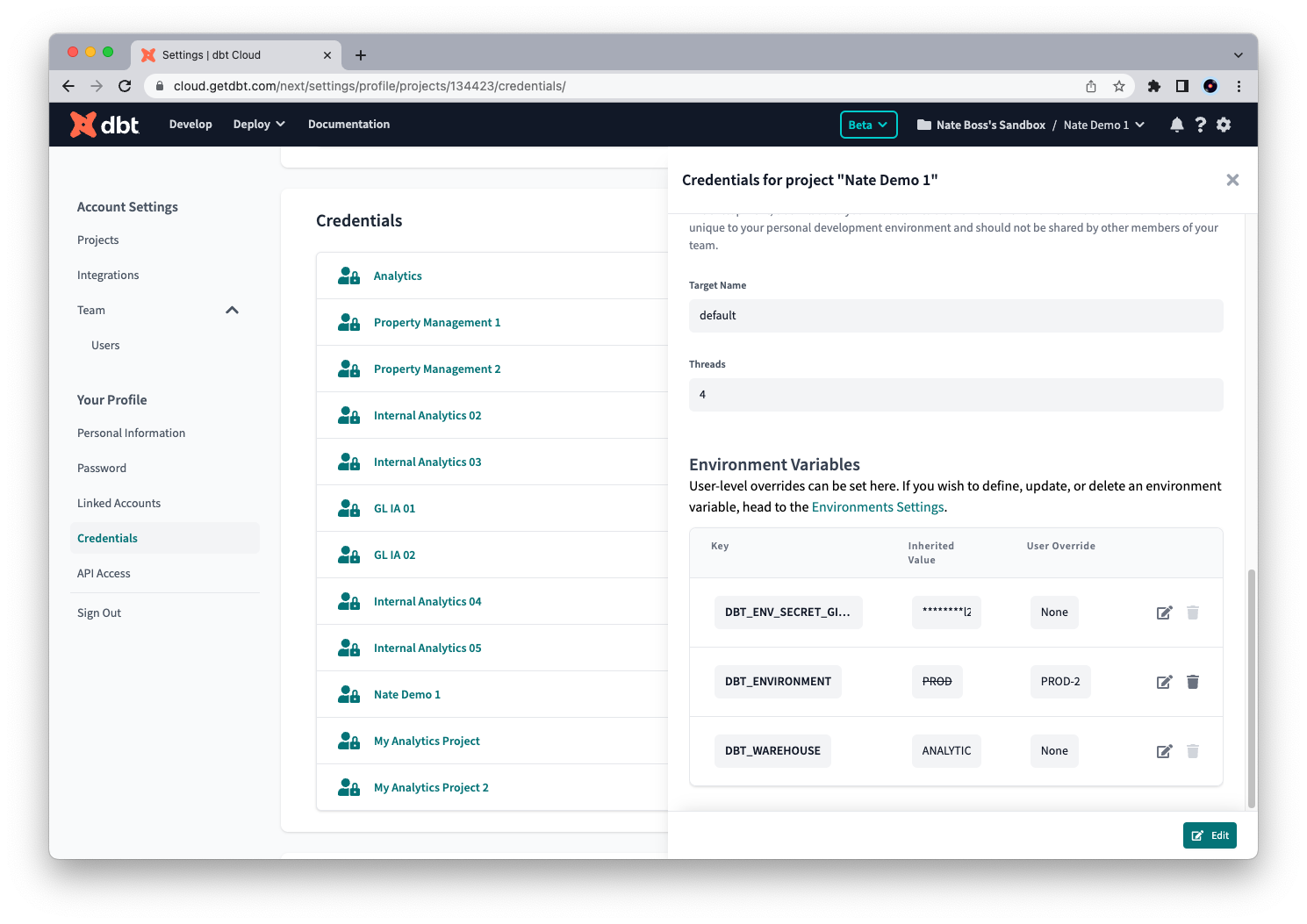
You can also set a personal value override for an environment variable when you develop in the dbt-integrated developer environment (IDE). By default, dbt Cloud uses environment variable values set in the project's development environment. To see and override these values, click the gear icon in the top right. Under "Your Profile," click Credentials and select your project. Click Edit and make any changes in "Environment Variables."
To supply an override, developers can edit and specify a different value to use. These values will be respected in the IDE both for the Results and Compiled SQL tabs.
If you have not set a project level default value for every environment variable, it may be possible that dbt Cloud does not know how to interpret the value of an environment variable in all contexts. In such cases, dbt will throw a compilation error: "Env var required but not provided".
If you change the value of an environment variable mid-session while using the IDE, you may have to refresh the IDE for the change to take effect.
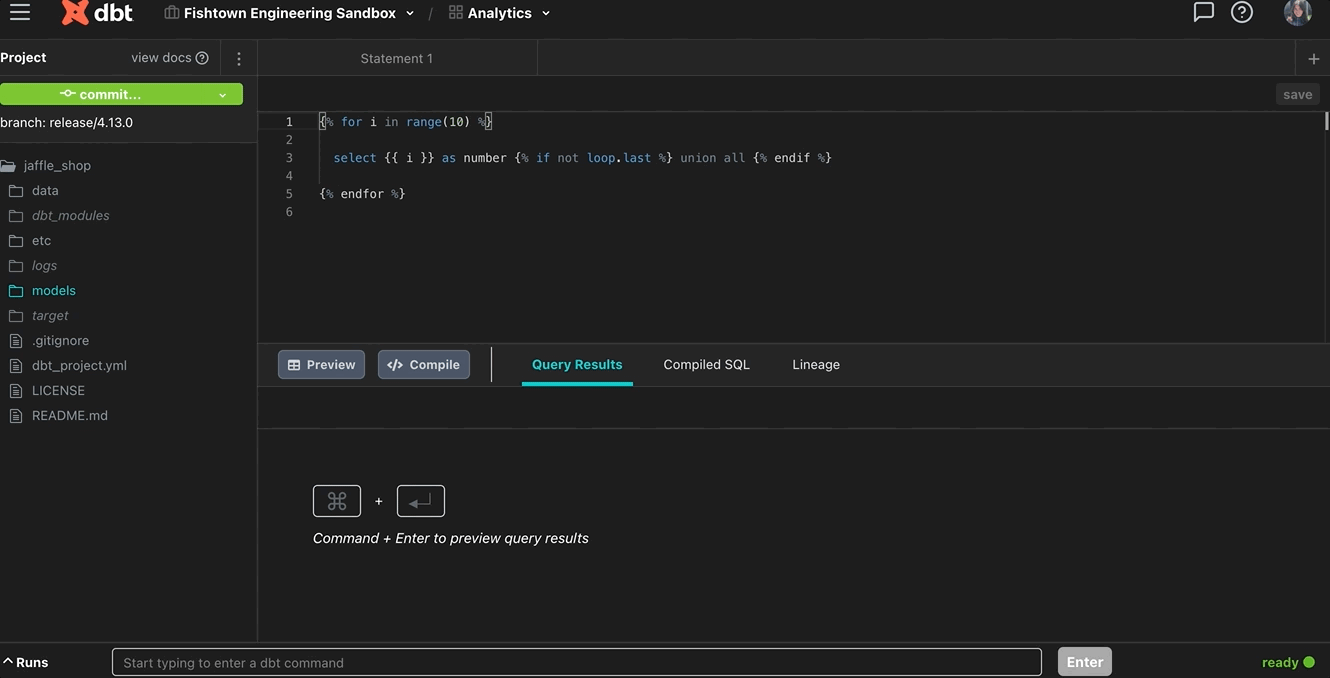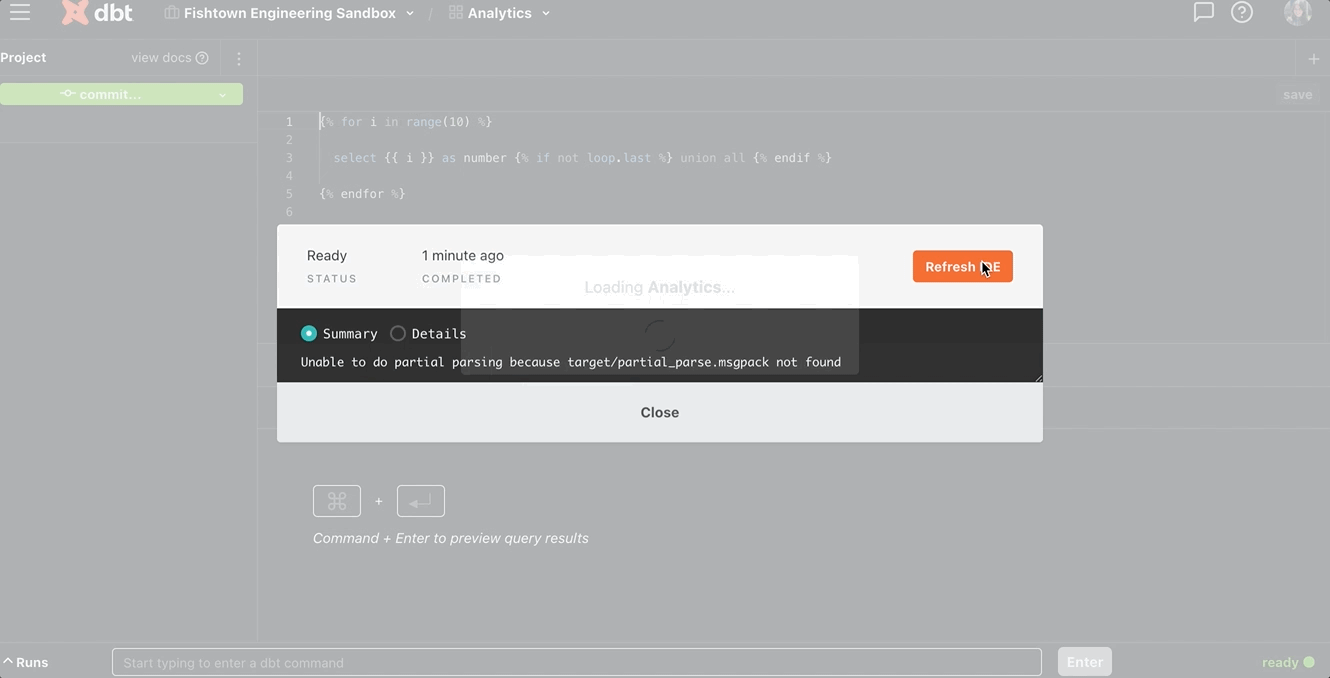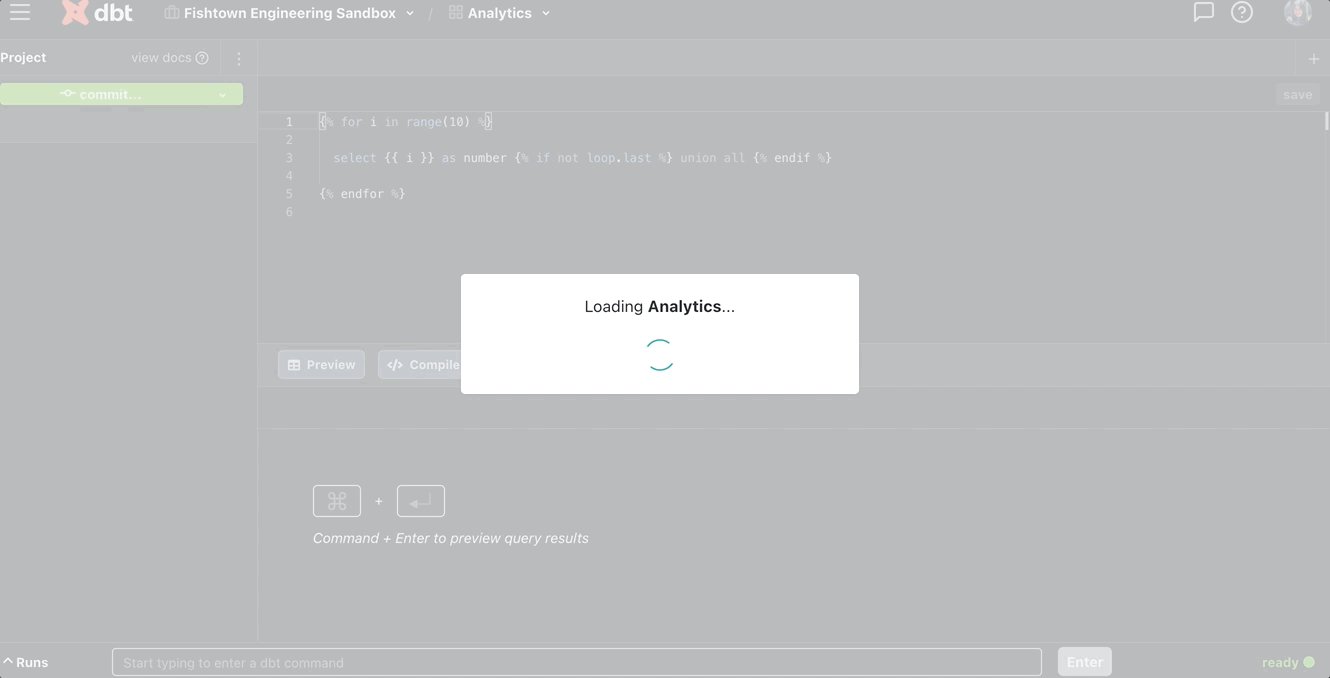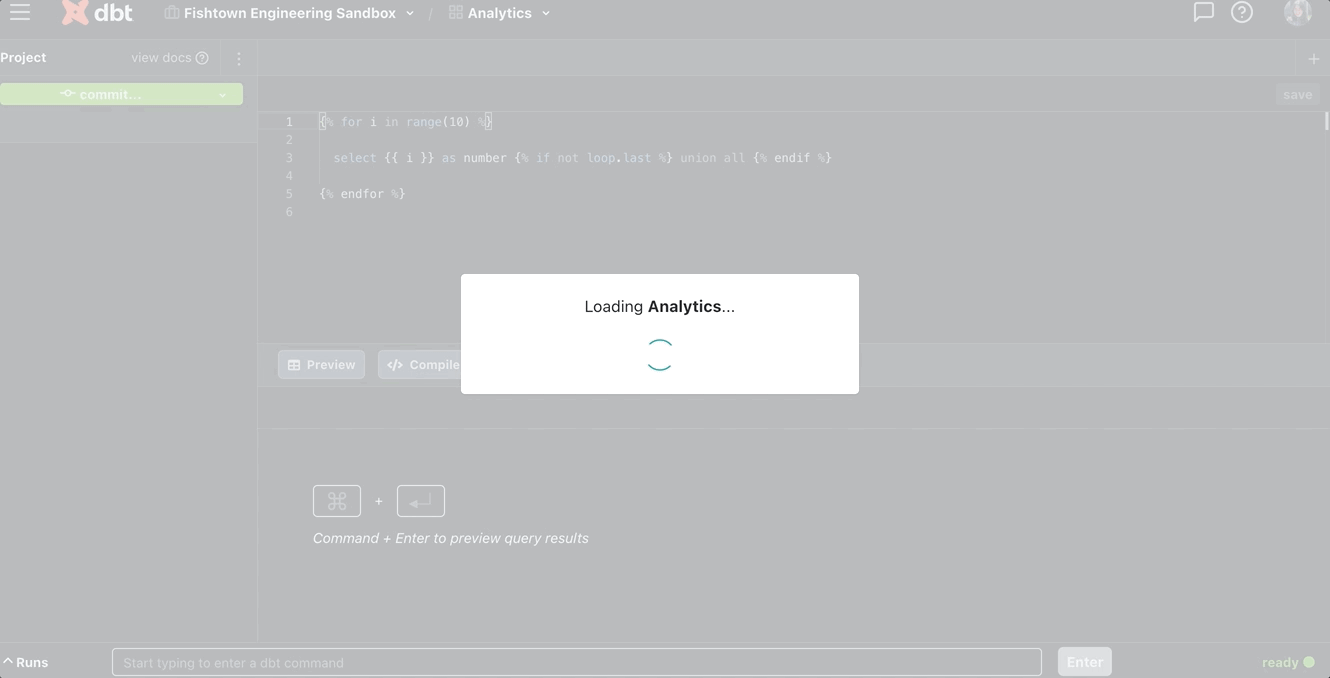
To refresh the IDE mid-development, click on either the green 'ready' signal or the red 'compilation error' message at the bottom right corner of the IDE. A new modal will pop up, and you should select the Refresh IDE button. This will load your environment variables values into your development environment.
There are some known issues with partial parsing of a project and changing environment variables mid-session in the IDE. If you find that your dbt project is not compiling to the values you've set, try deleting the target/partial_parse.msgpack file in your dbt project which will force dbt to re-compile your whole project.
Handling secrets
While all environment variables are encrypted at rest in dbt Cloud, dbt Cloud has additional capabilities for managing environment variables with secret or otherwise sensitive values. If you want a particular environment variable to be scrubbed from all logs and error messages, in addition to obfuscating the value in the UI, you can prefix the key with DBT_ENV_SECRET. This functionality is supported from dbt v1.0 and on.
Note: An environment variable can be used to store a git token for repo cloning. We recommend you make the git token's permissions read only and consider using a machine account or service user's PAT with limited repo access in order to practice good security hygiene.
Special environment variables
dbt Cloud has a number of pre-defined variables built in. Variables are set automatically and cannot be changed.
dbt Cloud IDE details
The following environment variable is set automatically for the dbt Cloud IDE:
DBT_CLOUD_GIT_BRANCH: Provides the development Git branch name in the dbt Cloud IDE.- Available in dbt v 1.6 and later.
- The variable changes when the branch is changed.
- Doesn't require restarting the IDE after a branch change.
- Currently not available in the dbt Cloud CLI.
Use case — This is useful in cases where you want to dynamically use the Git branch name as a prefix for a development schema ( {{ env_var ('DBT_CLOUD_GIT_BRANCH') }} ).
dbt Cloud context
The following environment variables are set automatically for deployment runs:
DBT_ENV: This key is reserved for the dbt Cloud application and will always resolve to 'prod'
Run details
DBT_CLOUD_PROJECT_ID: The ID of the dbt Cloud Project for this runDBT_CLOUD_JOB_ID: The ID of the dbt Cloud Job for this runDBT_CLOUD_RUN_ID: The ID of this particular runDBT_CLOUD_RUN_REASON_CATEGORY: The "category" of the trigger for this run (one of:scheduled,github_pull_request,gitlab_merge_request,azure_pull_request,other)DBT_CLOUD_RUN_REASON: The specific trigger for this run (eg.Scheduled,Kicked off by <email>, or custom viaAPI)DBT_CLOUD_ENVIRONMENT_ID: The ID of the environment for this runDBT_CLOUD_ACCOUNT_ID: The ID of the dbt Cloud account for this run
Git details
The following variables are currently only available for GitHub, GitLab, and Azure DevOps PR builds triggered via a webhook
DBT_CLOUD_PR_ID: The Pull Request ID in the connected version control systemDBT_CLOUD_GIT_SHA: The git commit SHA which is being run for this Pull Request build
Example usage
Environment variables can be used in many ways, and they give you the power and flexibility to do what you want to do more easily in dbt Cloud.
Clone private packages
Now that you can set secrets as environment variables, you can pass git tokens into your package HTTPS URLs to allow for on-the-fly cloning of private repositories. Read more about enabling private package cloning.
Dynamically set your warehouse in your Snowflake connection
Environment variables make it possible to dynamically change the Snowflake virtual warehouse size depending on the job. Instead of calling the warehouse name directly in your project connection, you can reference an environment variable which will get set to a specific virtual warehouse at runtime.
For example, suppose you'd like to run a full-refresh job in an XL warehouse, but your incremental job only needs to run in a medium-sized warehouse. Both jobs are configured in the same dbt Cloud environment. In your connection configuration, you can use an environment variable to set the warehouse name to {{env_var('DBT_WAREHOUSE')}}. Then in the job settings, you can set a different value for the DBT_WAREHOUSE environment variable depending on the job's workload.
Currently, it's not possible to dynamically set environment variables across models within a single run. This is because each env_var can only have a single set value for the entire duration of the run.
Note — You can also use this method with Databricks SQL Warehouse.
Env vars works fine with username/password and keypair, including scheduled jobs, because dbt Core consumes the Jinja inserted into the autogenerated profiles.yml and resolves it to do an env_var lookup.
However, there are some limitations when using env vars with Snowflake OAuth Connection settings:
- You can't use them in the account/host field, but they can be used for database, warehouse, and role. For these fields, use extended attributes.
Something to note, if you supply an environment variable in the account/host field, Snowflake OAuth Connection will fail to connect. This happens because the field doesn't pass through Jinja rendering, so dbt Cloud simply passes the literal env_var code into a URL string like {{ env_var("DBT_ACCOUNT_HOST_NAME") }}.snowflakecomputing.com, which is an invalid hostname. Use extended attributes instead.
Audit your run metadata
Here's another motivating example that uses the dbt Cloud run ID, which is set automatically at each run. This additional data field can be used for auditing and debugging:
{{ config(materialized='incremental', unique_key='user_id') }}
with users_aggregated as (
select
user_id,
min(event_time) as first_event_time,
max(event_time) as last_event_time,
count(*) as count_total_events
from {{ ref('users') }}
group by 1
)
select *,
-- Inject the run id if present, otherwise use "manual"
'{{ env_var("DBT_CLOUD_RUN_ID", "manual") }}' as _audit_run_id
from users_aggregated